- This article brings to focus the issue of water quality management
- Limits of water treatment can be obviated by smart water quality management.
- Reckless mining of resources has also caused contamination of the water bodies
- Appropriate water quality based on the application is important to ensure optimum utilization of resources and sustainable growth
- Nuanced policy framework is required to make sure the right quality and quantity is made available to the user
- The UDA framework is required to comprehensively manage the entire water quality aspect
Heading
Freshwater is going to be the most critical issue for human survival and wellbeing soon. The lack of it or too much of it, both are making life difficult for us. The urban flooding being seen in the recent times across cities, is a major cause of worry. The dry seasons see acute shortages and it is important to look at long term measures. The double whammy of excess and shortage at the same time, is a direct consequence of poor water resource management. The water resource management is certainly a concern area, however, this article brings to focus, the issue of water quality management.
Effective water resource management must have an integral component of water quality management to ensure calibrated usage of water based on the application and specific quality requirement.

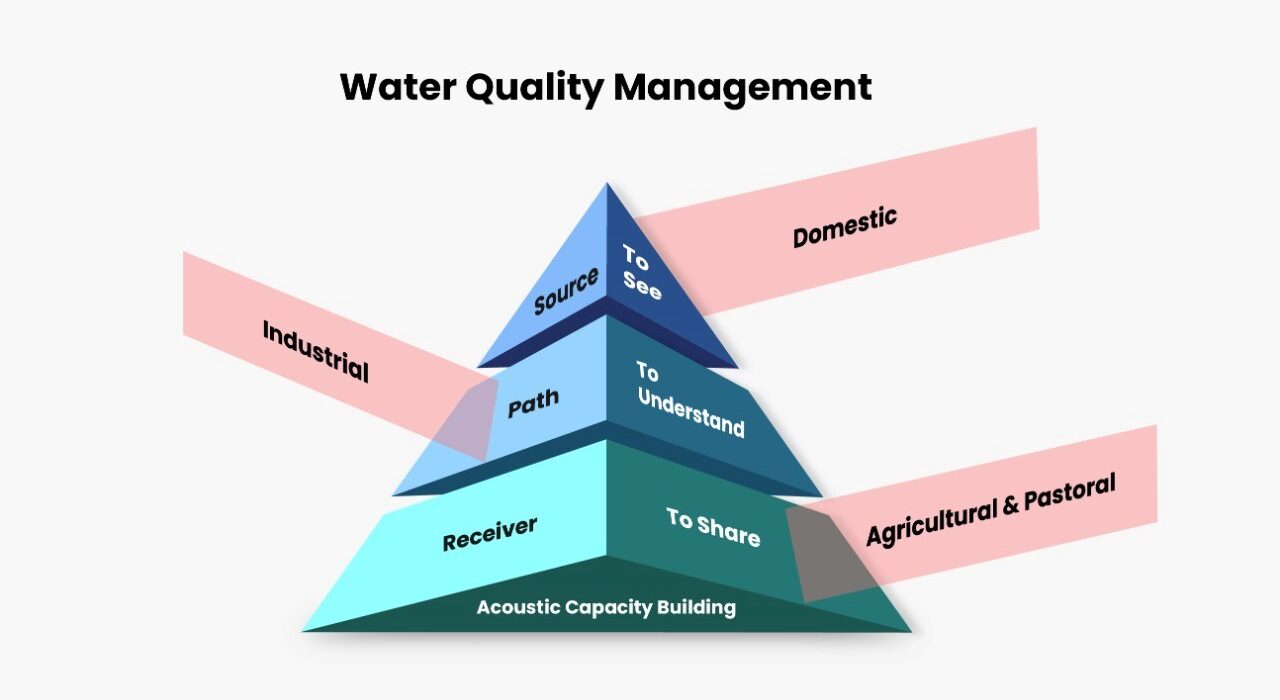
The conventional system does not have graded water availability across multiple applications. The same water is supplied for domestic, agricultural, industrial, re-creational and many more applications. In the domestic usage there is no difference in the water supplied for drinking and sanitation. The concept of real-time water quality assessment is yet to be introduced. When we analyze the water quality management issue, we need to drive the source-path-receiver model.
Source: The sources of water include ground water and surface water. As seen in the hydrological cycle, the multiple other sources like glaciers, rain (precipitation), and many more finally come down to settle in these two sources. The various human and natural activities have caused severe biological and chemical contamination of both the sources.
Let us discuss each of these causes to elaborate on the cause and effect:
Anthropogenic Impact: The agricultural practices of high use of fertilizers, pesticides, and multiple other chemicals over several decades without any impact assessment has caused massive levels of ground water contamination. The industrial discharges of harmful toxins, without proper treatment has caused severe degradation of the water bodies. The disposal of domestic and industrial waste without proper treatment further causes contamination of the water bodies through direct and indirect means. The reckless mining of resources has also caused contamination of the water bodies. Water bodies are easy dumping ground for waste and other material.
Natural Impact: In addition to the anthropogenic causes, the natural phenomenon like climate change, natural disasters and others also impact the water quality management. The climate change is directly impacting the hydrological cycle and thus causing unacceptable levels of contamination due to reduced water levels per unit contaminant. The natural disasters are putting the entire waste management system, out of gear and thus enhancing the contamination levels. Flooding, erosion, and many more natural disasters, cause serious contamination of the surface & ground water sources.
Path: The flow of the water from the source to the receiver is another cause of contamination. The massive urbanization has cause concretization thereby reducing the groundwater recharging at a massive scale. The unregulated waste disposal and use of chemicals across stakeholder, further causes massive contamination during this flow.
Receiver: The availability of the appropriate water quality based on the application is important to ensure optimum utilization of resources and sustainable growth. The consumer, must be made accountable for the usage and minimize wastage. The democratization of the water is a very tricky issue and needs a nuanced approach. The governance mechanism needs to be balanced and manage the local site specific socio-economic and socio-political realities. A nuanced policy framework is required to make sure the right quality and quantity is made available to the user.
The spatio-temporal real-time water quality monitoring becomes the most critical start point for any water quality management initiative. The data driven policy framework will allow good governance, necessary for any attempt at nuanced water quality management. The digitization of the entire water quality management will allow prediction of the future trends and facilitate well informed interventions. The contamination and the corresponding water quality degradation takes a long time, however once it sets in then it is extremely difficult to reverse. Thus, prediction will be a very critical aspect of the overall management in the long term. The Underwater Domain Awareness (UDA), in the holistic sense is thus, the key to water quality management.
To See will mean deployment of sensors at the appropriate location for continuous data gathering with adequate spatio-temporal resolution. The sensors with appropriate specification for comprehensively measuring all the water quality parameters will be required along with the platform to deploy these sensors at the appropriate location. These platforms could be static (buoys) or dynamic (Autonomous Underwater Vehicles) that could be deployed on surface and sub-surface. The ongoing ship borne or manual sample collection using boats is a sub-optimal method and cannot be scaled up to the level of automation required to deal with the present scenario.
To Understand: The data collected always has significant distortions due to sensor, medium and ambient noise. The pre-processing is important to make sure the data is free from any error. The pre-processing should have deep sense of the application, so that the useful information does not get lost during the cleaning process. The application specific processing is the next step and requires massive high performance computing infrastructure to ensure real-time data analytics. High end signal processing algorithms are required to generate precise and accurate output. At times, post processing is also required to manage the application and the data effectively for ascertaining the trends and develop mechanisms for precise prediction of the future events.
To Share The actionable output from the real data analysis must be made available in real-time to the user on the ground and the decision maker at the top level. The information must be user friendly and with clear instructions on the implementation. The Graphic User Interface (GUI) is another important requirement, that should be presented either on a hand-held device through a mobile application or on a large display with a sophisticated and versatile GUI. Customized GUIs for varied applications and user requirement will be critical.
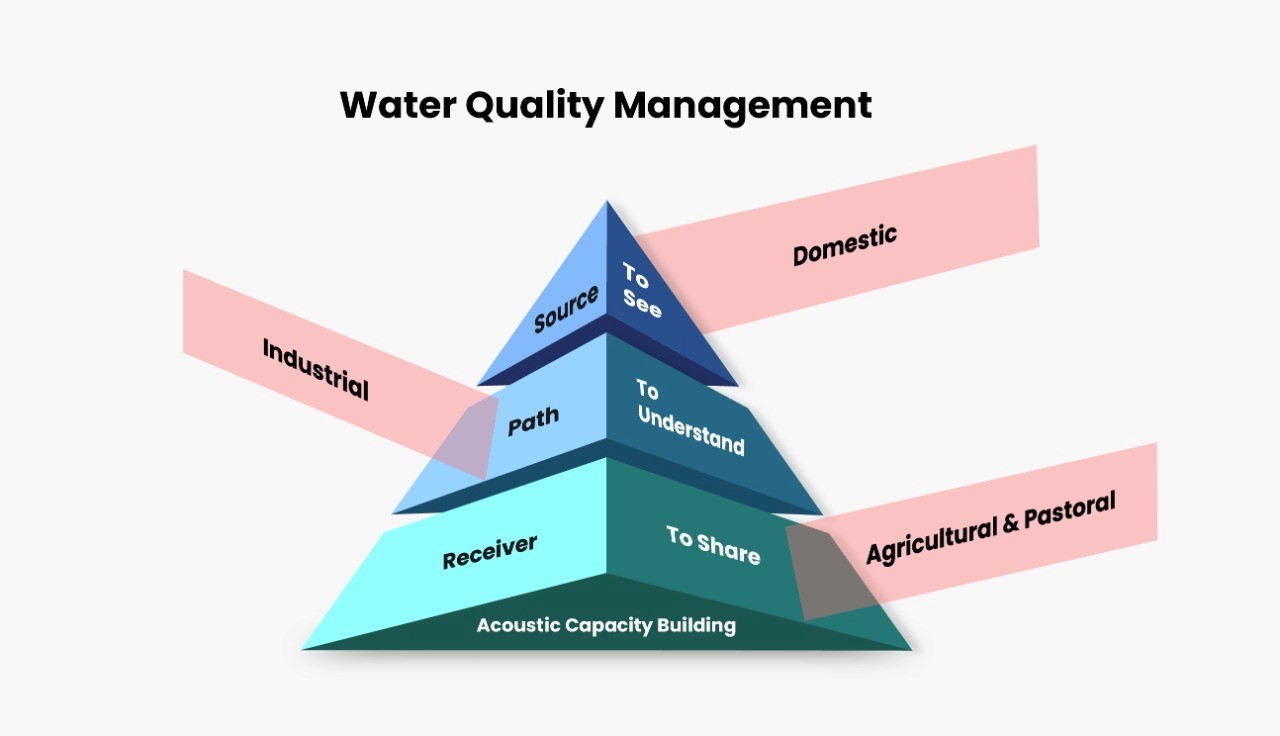
The three sides of the triangular cone represent the three stakeholders, namely the industrial, domestic and agricultural & pastoral. The to see, to understand and to share are the three fundamental steps for ensuring the UDA and the source-path-receiver model will ensure deeper understanding to better plan the interventions. The interventions will translate to policy & technology along with human resource development to justify the acoustic capacity & capability building.
The way ahead must be planned under a three-step formulation as discussed below.
Outreach: The outreach will include sensitizing of the stakeholders and decision makers on the nuances and relevance of the UDA framework for the entire water quality management requirement. The outreach will require webinars/seminars, workshops, and other means of interactions at multiple levels.
Engage: The stakeholders and decision makers need to formulate a structured engagement plan for optimum utilization of resources. The students and young professionals who will be the mainstay of this initiatives need to be prepared in a formalized manner to be able to take responsibilities in future. UDA fellowships at multiple levels will have to be announced that will be supported by the stakeholders and decision makers. This will allow direct and seamless integration of the young into the future career opportunities.
Sustain: The engagement with the stakeholders and the UDA fellows, must translate to meaningful interventions at both policy and technology levels. Projects and programs need to be initiated to build on the sustainable UDA framework for effective water quality management.
It is evident that the UDA framework is fundamental to the water quality management for a comprehensive solution to our freshwater crisis. The situation is going from bad to worse and could lead to strategic security concerns soon. The unequal distribution of freshwater is a serious concern and needs urgent measures to avoid any social unrest.

Dr (Cdr) Arnab Das
About Author
Dr (Cdr) Arnab Das, Director and Founder of MRC, Pune. Dr Das is a former Naval officer with 2 decades of active services and PhD holder from IIT Delhi with specialization in Underwater Acoustics. He has worked on several projects and has a plethora of publications to his credit.